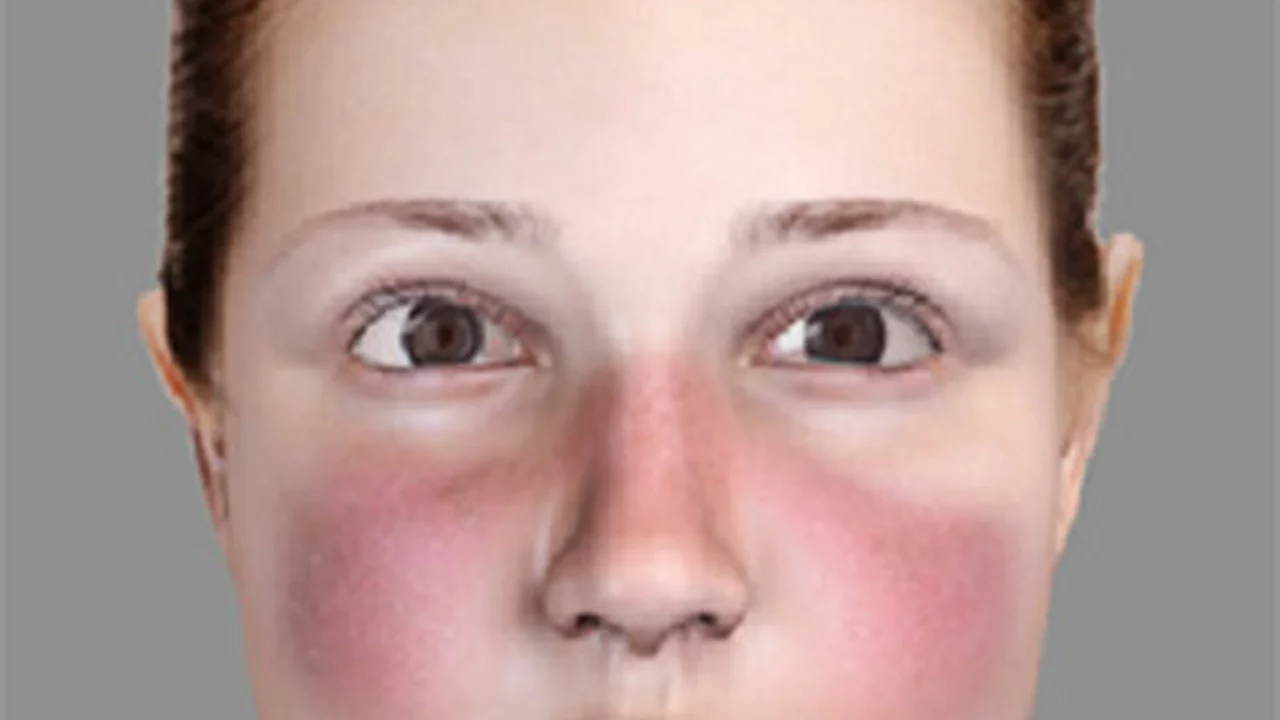
Understanding Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus Erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. It's a disorder where the body's immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. There are two types of Lupus Erythematosus: Discoid and Systemic. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a milder form that usually affects the skin, while Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a severe form that can affect several organs in the body.
Exploring the Role of Genetics in Lupus Erythematosus
Genetics play a significant role in the development of Lupus Erythematosus. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to the disease, which can be triggered by environmental factors. In this section, we will delve into the link between genes and Lupus Erythematosus.
The Influence of Inheritance in Developing Lupus
Lupus can run in families, suggesting that inheritance plays a role in the disease. However, it's not as simple as inheriting a single 'lupus gene'. Instead, it's a complex interaction of multiple genes, each contributing a small amount to the overall risk.
Identifying the Genes Associated with Lupus
Research has identified several genes associated with the risk of developing Lupus. These genes are involved in various functions, including immune response, DNA repair, and cell death. Understanding these genes can help us better understand the disease and develop more effective treatments.
Environmental Triggers in Genetically Predisposed Individuals
While genetics play a significant role, environmental factors are also critical in triggering the disease in genetically predisposed individuals. These factors include exposure to sunlight, certain medications, and viral infections.
The Relationship Between Ethnicity and Lupus
Lupus is more common in certain ethnic groups, suggesting a genetic component. It's more prevalent in people of African, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent compared to those of European descent. This section explores the genetic variations that might explain this disparity.
Genetic Testing for Lupus
While there's no definitive genetic test for Lupus, genetic testing can help identify individuals who are at a higher risk. However, it's important to remember that having a genetic predisposition doesn't guarantee that you'll develop the disease.
Understanding the Differences Between Discoid and Systemic Lupus
Although both Discoid and Systemic Lupus are forms of Lupus Erythematosus, they differ in their symptoms and severity. The genetics behind these two forms also differ, and understanding these differences can help in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
The Future of Genetics in Lupus Research
Genetics research in Lupus is still in its early stages, but it holds great promise for the future. It can potentially lead to new treatments and better diagnostic tools. This section will delve into the future possibilities of genetics in Lupus research.
Living with Lupus: Coping Strategies and Support
Living with Lupus can be challenging, but understanding the role of genetics can provide some comfort. It's also essential to have coping strategies and support systems in place. In this section, we'll provide some tips and resources for living with Lupus.

Comments
Matt Laferty
When you dive into the tangled web of lupus genetics, you quickly realize we are staring at a kaleidoscope of molecular interactions.
Each allele of the HLA region, each single‑nucleotide polymorphism in the interferon pathway, adds another brushstroke to a portrait that is as beautiful as it is terrifying.
The sheer number of risk loci uncovered in recent genome‑wide association studies makes the casual observer feel as if they have been handed a thousand‑piece puzzle with no picture on the box.
What’s more, the epigenetic modifications that sit atop these genetic predispositions act like mischievous gremlins, turning genes on and off in response to sunlight, infections, or even the humble stress of a missed deadline.
Patients of African or Asian descent often carry distinct haplotypes that explain, in part, why the disease runs hotter and more aggressively in those populations.
Yet, it is not enough to simply point at a gene and proclaim destiny; environmental triggers are the sly accomplices that whisper the final fatal note.
Ultraviolet light, for instance, can acutely stimulate cutaneous lupus lesions by prompting the release of apoptotic debris that the already‑confused immune system mistakes for foreign invaders.
Certain drugs, such as procainamide or hydralazine, have been shown to tip the delicate balance, unmasking latent autoimmunity in genetically susceptible individuals.
Viral infections, especially Epstein‑Barr virus, have the uncanny ability to hijack B‑cell maturation pathways, further fanning the flames of auto‑reactivity.
All of this culminates in a clinical picture where discoid lupus may remain skin‑deep, while systemic lupus erupts across kidneys, joints, and the nervous system, each manifestation echoing a different genetic chorus.
The future holds promise, however, as CRISPR‑based editing and polygenic risk scoring begin to whisper the possibility of personalized prevention.
Imagine a world where a simple blood test could flag a high polygenic burden, prompting early lifestyle interventions before the first rash appears.
Nevertheless, we must tread carefully, because tinkering with the genome carries ethical dilemmas as tangled as the DNA double helix itself.
In the meantime, clinicians should keep a keen eye on family histories, ethnic background, and environmental exposures when assessing lupus risk.
Only by weaving together genetics, epigenetics, and lived experience can we hope to tame this mercurial beast.
So, the next time you hear someone dismiss lupus as ‘just a skin condition,’ remember the invisible storm of genes raging beneath the surface.
Genie Herron
Ugh this whole genetics thing just drags me down why does my brain have to think about all this
Danielle Spence
Blaming genetics alone is a dangerous oversimplification; we must hold society accountable for environmental injustices that exacerbate lupus in marginalized groups.
It's morally reprehensible to ignore the socioeconomic factors that dictate exposure to UV radiation and limited healthcare access.
The scientific community has a duty to speak out against these systemic inequities.
Only then can we claim any progress.
Dhanu Sharma
It's interesting how the article stitches together genes and sun exposure the pattern is clear but we need more data the community will figure it out
Edward Webb
One cannot discuss lupus without acknowledging the lived experience of those who bear its burden.
The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers raises profound questions about determinism and free will.
While the science advances, patients often find solace in community support and shared narratives.
A nuanced understanding of risk does not diminish personal agency; rather, it empowers informed decisions.
Thus, clinicians should integrate genetic counseling with psychosocial resources.
In doing so, we honor both the molecular and the human dimensions of the disease.
Snehal Suhane
Oh great another endless lecture about genes like we needed more jargon – as if a handful of SNPs will magically solve the misery of lupus patients.
Maybe next you’ll tell us to eat kale and the disease will vanish, because that’s how science works, right?
Ernie Rogers
Our country should be pumping more money into lupus research instead of looking abroad it’s time we lead the charge.
Eunice Suess
Umm the sentence above has a few mistakes like its missing a comma after “instead of looking abroad” and “lead” should be “lead the charge” not “lead the charge.” Just saying.
Anoop Choradia
One must consider that the emphasis on genetic determinism may serve hidden agendas, redirecting public funds toward proprietary biotech ventures while sidelining holistic community health initiatives. Such stratagems are not unprecedented in the annals of medical history.
bhavani pitta
While the prevailing consensus lauds genetic research, one cannot ignore the potential perils of reductionist thinking that marginalizes socio‑cultural determinants. To place undue faith in polygenic scores is to gamble with lives, a gamble I deem ethically untenable.
Brenda Taylor
Wow another “deep” insight 🙄 sure why don’t we just ignore all that science and go with vibes instead
virginia sancho
Hey folks, great discussion here – if anyone’s looking for resources on support groups or reputable genetic counseling services, just shout and I’ll drop some links. Remember you’re not alone in this.
Namit Kumar
Thanks for the offer 😊 let’s also push for more domestic funding so we don’t have to rely on foreign labs for answers.
Sam Rail
Cool post, good stuff.